- 14
- Nov
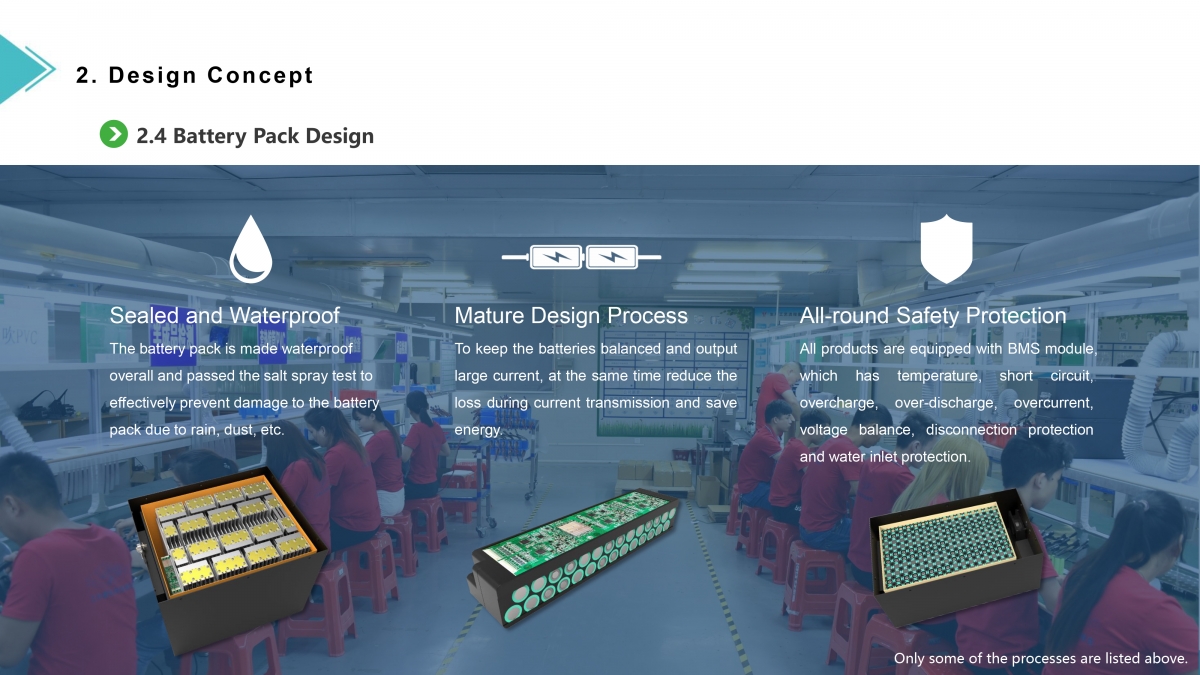
Advantages of lithium iron phosphate battery
The full name of lithium iron phosphate battery is lithium iron phosphate lithium ion battery, which refers to a lithium ion battery that uses lithium iron phosphate as a positive electrode material. There are many kinds of cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries, mainly lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganate, lithium nickelate, ternary materials, lithium iron phosphate and so on. Among them, lithium cobalt oxide is currently the cathode material used in most lithium-ion batteries, while other cathode materials have not been mass-produced on the market due to various reasons. Lithium iron phosphate is also one of the lithium-ion batteries. In terms of material principle, lithium iron phosphate is also an intercalation/deintercalation process, which is exactly the same as lithium cobaltate and lithium manganate.
Lithium iron phosphate batteries are lithium-ion secondary batteries. One of its main uses is as a power battery. It has great advantages over NI-MH and Ni-Cd batteries.
Advantage
1. Improvement of safety performance
The P-O bond in the lithium iron phosphate crystal is stable and difficult to decompose. Even at high temperature or overcharge, it will not collapse and generate heat like lithium cobalt oxide or form strong oxidizing substances, so it has good safety. A report pointed out that in the actual operation of acupuncture or short circuit experiments, a small part of the samples were found to burn, but no explosion occurred. In the overcharge experiment, high voltage charging that was several times higher than the self-discharge voltage was used, and it was found that there were still Explosion phenomenon. Nevertheless, its overcharge safety has been greatly improved compared with ordinary liquid electrolyte lithium cobalt oxide batteries.
2, improvement of life span
“Lithium iron phosphate battery” refers to a lithium ion battery that uses lithium iron phosphate as a positive electrode material.
The cycle life of a long-life lead-acid battery is about 300 times, and the highest is 500 times, while a lithium iron phosphate power battery has a cycle life of more than 2000 times, and it can be used for 2000 times with standard charging (5 hours rate). Lead-acid batteries of the same quality are “new half a year, half a year old, and half a year for maintenance”, which can take up to 1 to 1.5 years. When used under the same conditions, lithium iron phosphate batteries have a theoretical life of 7 to 8 years. Comprehensive consideration, the performance-price ratio is theoretically more than 4 times that of lead-acid batteries. High-current discharge can quickly charge and discharge high-current 2C. With a dedicated charger, the battery can be fully charged within 40 minutes of 1.5C charging, and the starting current can reach 2C, but lead-acid batteries have no such performance.
3, good high temperature performance
The electric heating peak of lithium iron phosphate can reach 350℃-500℃, while lithium manganate and lithium cobaltate are only around 200℃. Wide operating temperature range (-20C–75C), with high temperature resistance, lithium iron phosphate electric heating peak can reach 350℃-500℃, while lithium manganate and lithium cobaltate are only around 200℃.
4, large capacity
∩The capacity of rechargeable batteries will be quickly lower than the rated capacity when they are often fully charged and not discharged. This phenomenon is called the memory effect. Like nickel-metal hydride and nickel-cadmium batteries, there is memory, but lithium iron phosphate batteries do not have this phenomenon. No matter what state the battery is in, it can be charged and used without having to discharge it first.
6, light weight
The volume of the lithium iron phosphate battery of the same specification and capacity is 2/3 of the volume of the lead-acid battery, and the weight is 1/3 of the lead-acid battery.
7, environmental protection
Lithium iron phosphate batteries are generally considered to be free of heavy metals and rare metals (the nickel-hydrogen battery requires rare metals), non-toxic (SGS certified), non-polluting, in line with European RoHS regulations, and an absolute green battery certificate. Therefore, the reason why lithium batteries are favored by the industry is mainly due to environmental protection considerations. Therefore, the battery has been included in the “863” national high-tech development plan during the “Tenth Five-Year Plan” period and has become a key national support and encouragement project. With China’s accession to the WTO, China’s export volume of electric bicycles will increase rapidly, and electric bicycles entering Europe and the United States have been required to be equipped with pollution-free batteries.
But some experts said that the environmental pollution caused by lead-acid batteries mainly occurs in the company’s irregular production process and recycling process. In the same way, lithium batteries belong to the new energy industry, but it cannot avoid the problem of heavy metal pollution. Lead, arsenic, cadmium, mercury, chromium, etc. in the processing of metal materials may be released into dust and water. The battery itself is a kind of chemical substance, so it is possible to produce two kinds of pollution: one is the pollution of process excrement in the production engineering; the other is the pollution of the battery after it is scrapped.
Lithium iron phosphate batteries also have their shortcomings: for example, poor low-temperature performance, low tap density of the cathode material, and the volume of the lithium iron phosphate battery of equal capacity is larger than that of lithium-ion batteries such as lithium cobalt oxide, so it does not have an advantage in micro-batteries. When used in power batteries, lithium iron phosphate batteries, like other batteries, need to face battery consistency issues.
